We’ve all searched Excel via the GUI for values and strings. Usually we’re just looking for a single cell and then we go on our way, but you can also code the search behavior in VBA to automate the process. This is useful when building customized dashboards, a specific algorithm or a repetitive find and replace process.
The key to using VBA to find matches in cells is Range.Find, a method that searches the range and finds what you’re looking for - with plenty of options, too.
The Method and the Range
First, the Range.Find method is a method that acts on a Range object. Therefore, you must know which part of which sheets and workbook you want to target. Set the range with a start and end cell or use an entire column. We’re going to slowly build our Find function, starting with ways to specify the range you want to search.
Range("A2:D500").Find 'starts from Row2/Col1 and goes to Row500/Col4
Range("A:D").Find 'starts in Row1/Col1 and goes to the final row in Col4Using an entire column means you don’t have to specify the starting or ending rows - they’ll all be included.
An Essential Test
Since the return value is either Nothing or a Range object (it will be a cell), and we usually want to access properties of the object, it makes sense to set the output to an object, like this:
Dim foundCell as Range
Set foundCell = Range().FindThen we can conveniently access the properties of .Address, .Row or even its .Value. However, because the output is Nothing when there are no matches, we must check for this condition before attempting to access these properties:
If foundCell Is Nothing Then
'code to handle not finding a match
Else
'code to handle the match, such as foundRow = foundCell.Row
End IfMake powerful macros with our free VBA Developer Kit This is actually pretty neat. If you have trouble understanding or remembering it, our free VBA Developer Kit can help. It’s loaded with VBA shortcuts to help you make your own macros like this one - we’ll send a copy, along with our Big Book of Excel VBA Macros, to your email address below.
Why Use .Find at all?
The first reason to use .Find is efficiency. Built-in methods are almost always more efficient than the programmer’s code because Microsoft’s team has specifically optimized their calculations. Could you write a for-loop to look in your range and find the needed values? Sure. You could also read the values into an array. But these are not as efficient as using the built-in VBA method designed specifically to search the range.
Another reason to use .Find is to automate a process. Using the GUI to find cell locations is fine if you only have a few cells to check. But what if you have thousands and need to write all those locations into another file (using OpenTextFile)? .Find will let you automate this process.
Finally, while the Excel GUI is well-designed and powerful, you may be building a custom dashboard. To align the layouts and styles, you may want to build your own search GUI. You can still leverage the efficiency of the .Find method on the backend while your users see your custom frontend UserForm.
Range.Find Parameters
So far we’ve only presented pseudo-code to help paint the big picture of what a Range.Find macro should include (specifying the range, setting the output to a range variable, and checking for nothingness). The Range.Find method itself accepts quite a few inputs but only requires one: What.
- What - the thing you’re looking for. This accepts strings but also numbers. Note that operators (<, >, =, etc.) are not accepted unless part of a string
- After - starts searching after this cell (and excludes this cell until it loops around)
- LookIn - search the values (
xlValues) or formulas themselves (xlFormulas). Sometimes used for comments, too (xlComments,xlCommentsThreaded) - LookAt - used to match part of the cell (
xlPart) or force a full match (xlWhole) - SearchOrder - search an entire row (
xlByRows) or an entire column (xlByColumns) first before moving to the next - SearchDirection -
xlPreviousorxlNext, to navigate away from theAftercell - MatchCase - whether the case must be a perfect case-sensitive match or not (True or False)
- MatchByte - matching by character type (True or False)
- SearchFormat - True or False to search in cell formats and requires a separate line of code
Important: VBA saves your settings for LookIn, LookAt, and SearchOrder on every run, including by the GUI. Since users who interact with the GUI may make changes, good coding practice dictates hardcoding these parameters every time you use them in your macro.
What
Finding strings is straightforward. Simply enclose the necessary string in quotes. You can even use this to find parts of formula. For example, Column G may contain a user’s total purchases and a formula may exist, like What parameter.
What can also be a number. One example is to find order numbers in a list and use that to produce the associated customer name, using something like VBA Offset. This could also be used to find part numbers in a big sheet of part IDs.
After
The search begins AFTER this argument. This argument should also be a cell, such as
LookIn
This lets you choose whether you want to match the cell value, the cell formula, or the comments associated with the cell.
Most commonly we use xlValues, but we may want to find a formula so that we can change it. This also becomes important to set if we have cells that dictate text via formula, such as "VIP" in the code) we must pass xlValues to LookIn. If we passed in (or used a saved setting) xlFormulas, we’d get each cell containing this IF-statement.
LookAt
This lets you match part of or the whole cell value (or formula or comment).
For example, you may have multiple words in a cell (or very likely in comments). If your code can only captures a single word (perhaps a user can only remember part of the comment), then you can use xlPart to find any partial match.
If you’d like, you can insert wildcard characters * into the string to effectively induce xlPart behavior with xlWhole.
Set x = Range("A:K").Find(What:="check", LookIn:=xlComments, LookAt:=xlWhole) 'the entire comment must be the single word check
Set x = Range("A:K").Find(What:="check", LookIn:=xlComments, LookAt:=xlPart) 'find all comments with "check" in them
Set x = Range("A:K").Find(What:="*check*", LookIn:=xlComments, LookAt:=xlWhole) 'functionally equivalent to immediately preceding statementSearchOrder
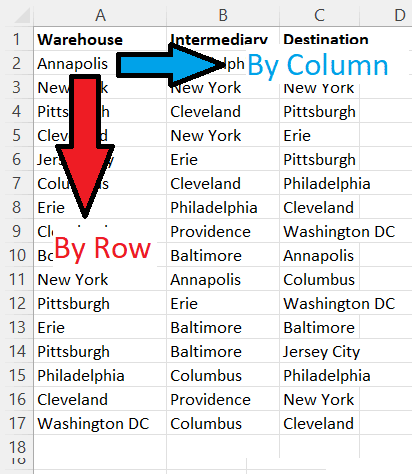
Use this argument to choose to search by columns or by rows. For some applications this is not very useful, but in others, it may be essential.
When you have multiple cells with similar entries, especially if you are using xlPart, you may have multiple hits. You may also want to exhaust an entire column or row before moving to the next. You could achieve this by using one line of code to target each row or column, but that is unwieldy. Setting SearchOrder is much more efficient.
Search down the rows or across the columns
With the image above in mind, when you set xlByRows, you will check each cell in Column A, and only when the data in Column A is exhausted will Range.Find move to Column B. Conversely, setting xlByColumns will look across the columns, starting in Row 1 and continue until all columns are exhausted before moving to Row 2.
SearchDirection
This parameter sets whether Excel moves down and to the right or up and to the left from your starting cell. If you haven’t set After, then the upper-left corner of the range marks the starting point. Knowing this is useful when you’re running .Find in a loop.
Remember that this parameter’s choice is saved at the application level, so when you run another Range.Find line, whether in another part of the code or as part of a loop, Excel will continue in the same direction.
MatchCase and MatchByte
MatchCase toggles case matching. This might be beneficial if your data formatting standards rely on case, such as all-caps for headers. Using UCase and the header names would help you identify header rows in a large sheet. It could also be used to find “important” comments where the commenter has written everything in capital letters.
MatchByte is used for matching characters, specifically of languages that have too many characters for single-byte data formats. English and other European languages can encode their alphabets using one byte (8 bits) of data. For some languages, like Mandarin, where an alphabet doesn’t directly encode the language’s sounds in an alphabet, more bytes are needed, and hence the use of MatchByte could be beneficial.
Both of these properties are technically of Variant type, but they use True and False, just like a Boolean data type.
SearchFormat
This parameter lets you search formatting, such as bold or large font, for key information. You could even use it for cell fill colors, like if you highlight all
Don’t forget to clear the FindFormat format before starting, just in case.
Application.FindFormat.Clear
Application.FindFormat.Interior.Color = vbYellow
Set foundCell = Range("A:K").Find(What:="*", SearchFormat:=True)If you don’t know the text for a cell (in value, comment, or formula), you can search solely on formatting by using the wildcard, which will match any text (excluding empty cells). Searching an empty string will help you find the blank cells.
Using the Return Value
If a match exists, Excel will return a cell as a Range object. With this, you can access any property that a range would reasonably have.
One example is substituting .Find as a database relation and using the input as a kind of foreign key. Let’s look at an example.
Say you have one sheet with orders, names, and customer IDs, and a second but password-protected sheet that stores customer details. Moreover, you have three access levels for employees: level-1 sees only orders, level-2 sees orders and customer phone numbers, and level-3 sees complete customer and order details.
In this case you may use a VLOOKUP to display names next to orders, linking them by customer ID, but you don’t want to display customer phone numbers to level-1 employees. In this case, you could create a password-enabled dashboard, then use .Find to output the customer’s phone number based on the ID. This would give level-2 employees a way to access phone numbers but protect further details, like customer addresses.
This pseudocode makes orderNum act a bit like a foreign key in a database:
orderNum = functionToGetOrderNumber
Set foundCell = Sheets("Customer Details").Range([customer details range]).Find(orderNum)
customerPhone = Sheets("Customer Details").Cells(foundCell.Row, customerPhoneColumn)Finding all matches
Range.Find can be as simple as returning the first match of a string, but the optional arguments available make the method very versatile, too. Strings are permissible but so are other data types, and you can search through cell values but also cell formulas and even comments. The option to search for a specific format works, too, and using the wildcard for What here essentially converts Range.Find into a format finder.
You’ll notice that each instance of Range.Find only finds the next item. If you want to find all the cells matching your search criteria, you can combine Range.Find with Range.FindNext inside a loop and you can join all the found cells with the VBA Union method.
To help you build your own application using all of these methods, here’s a working code you can customize for your own needs:
Sub FindAll()
Dim foundCell As Range 'single cell
Dim foundCells As Range 'all found cells
Dim searchCells As Range 'range you want to search
Dim celladdress As String 'just used so you know when you've found everything
Set searchCells = Range("A:E")
Set foundCell = searchCells.Find(What:="check", LookIn:=xlValues, LookAt:=xlPart)
If foundCell Is Nothing Then
'code to handle not finding a match
Debug.Print ("no match found")
Else
'find all other matching cells with FindNext
celladdress = foundCell.Address
Set foundCells = foundCell
Do
Set foundCell = searchCells.FindNext(foundCell)
Set foundCells = Union(foundCells, foundCell) 'combine found cells
Loop While celladdress <> foundCell.Address
Debug.Print (foundCells.Address)
End If
End SubAt the end of this routine, all cells containing your search parameter will be stored in the Range object