In part 4 of our Python OS series, we’re going to start creating and deleting files and folders so you can take full control of your system’s directory structures.
- Part 1 of our series on the Python OS module described how to use chdir and getcwd to set your current working directory.
- Part 2 demonstrated how to list all files and folders in a directory using Python OS.
- Part 3 showed you how to open files with their native applications using Python OS.
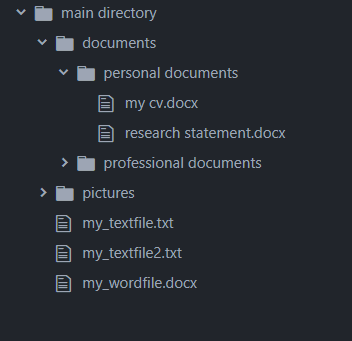
As with all the other tutorials in this series on the Python OS module, we’ll be using the following directory structure as our basis:
Our first tutorial left off with our current working directory set to
import os
os.chdir(r"C:\main directory")
wd = os.getcwd()Creating and Removing Files and Folders
Create Folders with Python OS
To create a folder or a directory with Python, use the mkdir() method. You simply need to pass the folder name to the method. The following script creates a folder named games() in your current working directory.
Next, you can use the listdir() method to print a list of files and folders in your current working directory.
Notice, if you do not pass any path to the listdir() method, it prints the contents of your current working directory.
import os
os.mkdir(r"games")Now, you can use the listdir() method to print a list of files and folders in your current working directory. If you don’t pass a path to the listdir() method, it prints the contents of your current working directory.
print(os.listdir())The output below shows that the folder games has been created.
['documents',
'games',
'my_textfile.txt',
'my_textfile2.txt',
'my_wordfile.docx',
'pictures']You can also pass the full path to the mkdir() method, but just know the method doesn’t act recursively. For example, in the following script, if
import os
os.mkdir(r"C:\TestFolder\MyGames")Here’s how to get around this limitation. Since the mkdir() method can only create a folder at the top level inside another directory, you can instead use the makedirs() method to make multiple folders at deeper levels at the same time.
For instance, the following script will create a folder named
import os
wd = os.getcwd()
os.makedirs(wd + r"/games2/new_directory")
print(os.listdir())Output:
The output shows the newly created
['documents',
'games',
'games2',
'my_textfile.txt',
'my_textfile2.txt',
'my_wordfile.docx',
'pictures']To see if the contents of the
print(os.listdir(r"games2"))You can see the newly created folder
Output:
['new_directory']Before we start making files, I just want to demonstrate that the makedirs method works to create recursive folders with full file paths, too. Using our failed example from earlier, you can run the following script to create a
import os
os.makedirs(r"C:\TestFolder\MyGames")Code More, Distract Less: Support Our Ad-Free Site
You might have noticed we removed ads from our site - we hope this enhances your learning experience. To help sustain this, please take a look at our Python Developer Kit and our comprehensive cheat sheets. Each purchase directly supports this site, ensuring we can continue to offer you quality, distraction-free tutorials.
Create Files with Python
Okay, let’s now create a file inside the open() method, like this.
file = open( r'games2/new_directory/myfile.txt', 'w+')
file.close()Running the above script will create the
To see if your file was actually created, list the contents of your
import os
print(os.listdir(r"games2/new_directory"))Output:
['myfile.txt']Removing Files and Folders with Python OS
Before you remove a folder with Python, you need to remove the files inside it. Let’s try to remove the remove() method for that, as shown below:
import os
os.remove(r'games2/new_directory/myfile.txt')
print(os.listdir(r"games2/new_directory"))You’ll notice the
Output:
[]Once the directory is empty, you can use the rmdir() method to delete the folder by passing the directory path to the rmdir() method. The following script removes the
import os
os.rmdir("games")
print(os.listdir())The output below shows that the “games” folder was successfuly removed.
Output:
['documents',
'games2',
'my_textfile.txt',
'my_textfile2.txt',
'my_wordfile.docx',
'pictures']Similar to the mkdir method, the rmdir method will only remove the inner most directory if your path contains multiple folders. For instance, the following script will only remove the
import os
os.rmdir(r"games2/new_directory")
print(os.listdir())Output:
['documents',
'games2',
'my_textfile.txt',
'my_textfile2.txt',
'my_wordfile.docx',
'pictures']Finally, the script below removes the “games2” folder from your current working directory.
import os
os.rmdir("games2")
print(os.listdir())Output:
['documents',
'my_textfile.txt',
'my_textfile2.txt',
'my_wordfile.docx',
'pictures']If you enjoyed this series on the Python OS module, be sure to subscribe using the form below for more Python tips and tricks.
Code More, Distract Less: Support Our Ad-Free Site
You might have noticed we removed ads from our site - we hope this enhances your learning experience. To help sustain this, please take a look at our Python Developer Kit and our comprehensive cheat sheets. Each purchase directly supports this site, ensuring we can continue to offer you quality, distraction-free tutorials.